Information Technology Software Solutions for Healthcare Industry

While healthcare is at times misunderstood to be a direct link between illnesses and their standalone treatments, that’s not the case.
Ideally, any system of medicine should be constructed as an unbiased, comprehensive unit responsible for curing diseases or improving the quality of a patient’s remaining life, alleviating pain, making care accessible, reducing wastage of time.
You get the drift.
We aren’t there yet. But, we have evolved impressively in defining a multidimensional medical management system which caters to different needs and sectors at once. Health Information Technology is the contribution of this decade to our current system of medicine.
The Benefits of Information Technology in Healthcare
Look at it as a combination of technological tools, healthcare objectives, and business practices.
The outcome of every Health IT manoeuvre is to enable high-quality care in an error-free, effective manner. Mostly, that aim is achieved by digitising every piece of available patient information, connecting medical care facilities across the globe irrespective of their locations, and introducing reliable access to medicines and diagnosis using technology.
For the Patients, this means:
- Complete and updated documentation
- Quick access to records
- Coordinated, reliable healthcare
- Reduced paperwork
- Easier interactions
- Convenient billing and prescription retrieval processes
For the Hospitals and Medical Professionals, this means:
- Improved patient care attributes like safety, communication, timeliness
- Better diagnostics
- Liability prevention
- Risk management
- Reduced wait time
- Streamlined workflows
- Integrated patient tracking
- Care personalisation
- Reduced paperwork
- Cost-saving
The advantages are numerous, the possibilities endless.
However, to better understand how the uses of information technology in healthcare can lead to such outcomes, you must recognise the types of health information technology.
Categories of Healthcare Information Technology
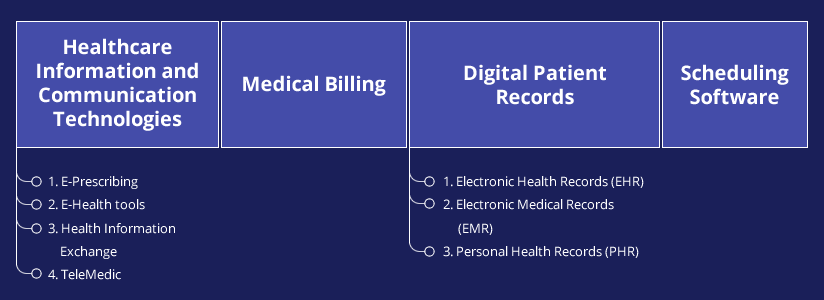
1) Healthcare Information and Communications Technologies
Every digital technology that supports recording, storing, processing, and exchanging information about the health sector comes under the umbrella of ICT. Specifically, it involves electronic prescribing, web-based health tools, telemedicine, and continuous flow of information.
ICT is promoted in the health sector mostly because it has the potential to create a high quality, well connected, patient-centred healthcare at reasonable costs.

A) E-Prescribing
Ideally, every prescription ever generated would be checked against the current medication, diagnoses, allergies, weight, etc. of the patient. However, it isn’t always possible considering the obstructions like:
- The lack of a thorough record of the patient’s medical history
- Illegible prescription handwritings
- The lack of information about a patient’s prescription orders, reorders, and refills
E-Prescribing systems, along with other elements of health IT, attempt to create a closed loop of communication between the doctors and patients.
Pros:
- As an interactive data transaction, it maintains a profile of every patient’s medication
- It saves time as the pharmacists can check with the clinic to verify the prescription using the software
- Reduced medication errors like adverse drug reactions because of the wrong medication
- Increased safety, accuracy, patient satisfaction
- Better processing efficiency and rapid prescription fulfilment
Anyhow, the system still needs trained professionals to run an E-Prescribing software effectively. Then, there are issues like inaccurate e-prescriptions, problems with the software design or E-prescribing vendors, and costs associated with their maintenance and transactions.
B) E-Health tools
Web-based e-health tools are services available to the public for recording personal health data and tracking treatments etc. they contribute to an emerging system that supports the growing consumer e-health phenomenon.
As a public channel that facilitates remote interaction with medical professionals and lets people take responsibility for the consistency of their health data, E-health tools are a method to cope with the fragmented healthcare system.
Pros
- They offer a spectrum of well-defined health information
- They help people track diseases and communicate with the healthcare provider
- They may be designed to support a specific health-related behaviour change, like stopping alcoholism, smoking, etc.
- They initiate interaction among various internet communities, offer social support, and help people exchange information among groups with a similar agenda
- Many tools provide structured support to help the customers weigh the consequences of their decisions while evaluating a health program or managing other healthcare aspects
As per a randomised trial including patients with metastatic tumours, the users of E-health tools were reported to show better life quality and survival chances. A possible explanation could by timely clinical intervention because of due maintenance of body and symptom changes.
At the same time, using these E-health tools to self-diagnose can easily backfire. For the system to get adopted all over, we need more strict and well-defined regulations surrounding the matter.
C) Health Information Exchange
On every level of a health care system, an information exchange plays a crucial role. It extends the ability to move clinical information electronically among many health-related information systems. This access allows for timely and hence more efficient patient care on many fronts.
Pros
- An HIE evolves with new information and time
- It supports interoperability among healthcare providers, technological professionals, and patients
- The well-vetted information reduces redundancy, errors, and unnecessary testing, resulting in improved patient safety and care efficiency
- Judicious use can help support clinical decision making and reduce related costs
Micky Tripathi, CEO, Massachusetts eHealth Collaborative, had predicted the third generation of HIEs to be centred around more than just the technology of the year.
In addition to including IOT, cloud, connectivity, and automatic market adjustments, HIE 3.0 will also be very engaging. It’ll integrate social determinants, incorporate behavioural health as a facet of medical data, and relate cost with quality more effectively.
D) TeleMedic
Telemedicine is significantly related to the use of technology to provide remote medical services. It highlights the use of technologies like phone calls, emails, video chats, etc. to connect patients to medical help and eliminates the need for in-person visits.
Pros
- It helps deal with issues like shortage of doctors and medical help in rural areas
- It arms small hospitals to offers intensive care despite having a small staff
- It helps patients save time and offers a convenient on-demand healthcare
- It helps reduce healthcare costs for all parties involved
- It’s patient-centred, offers timely diagnosis, encourages earliest possible treatment, and improves care quality
The global telemedicine market could easily cross USD 48.985 billion by 2021, predicts Research and Markets.
However, the system isn’t flawless. We still need better-networked relationships between independent health entities. Often, top-level administration support becomes a factor of resistance in implementing a successful telemedicine system. Also, there is an immediate requirement of better guidelines and standards.
Also Read Our Page: Hire developers in India
2) Medical Billing
Every insured patient’s visit to the doctor is a transaction between the patient, healthcare provider, and the insurance company. Medical billing is the part of Health Information Technology which negotiates payment between these three parties and sees to the fulfillment of the arrangement.
Revenue Cycle Management
For every office visit where a doctor diagnoses a patient and updates his/her medical records, the medical codes are assigned accordingly. The updated bill is transmitted to the insurance payer via Electronic Data Interchange as a claim. It’s reviewed and validated by the insurance company.
The approved claims are reimbursed. The rejected claims are reverted. The health care provider may appeal for the reconsideration of denied forms. It must research and rectify the errors in the rejected forms and resend them to the payer.
Pros
- An excellent medical billing software can save money by limiting the cost of hiring of support staff and billing expenses
- It reduces the stress of managing billing, letting the staff focus on improving the workflow
- Medical billing services also take care of credentialing and enrollment processes for new practices
- As the billing service and health records software are interconnected, it encourages transparent functionality
Cons
- Amidst increasing billing costs, it is imperative to calculate ROI before adopting any medical billing service to ensure continuous returns
- Using the software will require training that most service providers may provide upon enquiring
- In specific cases, a patient with debts, for instance, the billing procedure may get complex
3) Digital Patient Records

It’s an electronic data store for patient accounts. It can include a good range of information. It’s accurate, time-stamped, easier to share across a network, and super convenient for tracking patients.
But, above all, Digital Patient Records are a critical entity in the Health IT ecosystem for one reason- global adoption.
The 2017 Physician Workforce Survey released by the Canada Medical Association revealed that 64% of primary care physicians in the country use electronically transmitted discharge reports. The United States CDC reports that over 80% of US hospitals had adopted one or the other kind of digital records by 2014. The Indian government has proposed a National eHealth Authority to standardise the use of digital patient records in the country.
The point- Everyone seems to like the idea of a single database with information related to several patients.
You’ll find three kinds of digital patient records in Health IT.
A) EHR or Electronic Health Records
An EHR is the systemised, digital arrangement of patient data owned by a hospital. It was developed to standardise error-free medical documentation that’s usable in the long-term.
EHR exhibits several advantages over handwritten records. Notably, nobody has to worry about the legibility of the written word, reducing the chances of a medical error. The electronic records are portable and follow specific rules regarding terminology and data input.
Pros
Data Accessibility
The patient data is available to everyone at all times. It can be shared across a network. The system is free from data duplication, batch delivery, and information loss during transfer.
Improved Storage
An EHR eliminates the requirement to maintain physical storage for patient info. There is no need to transport, sort, stamp, or deliver files between medical care centres.
Standardisation
EHR favours standard record keeping. It encourages storing detailed information about a patient’s medical history, demographics, prescriptions, allergies, test results, physician notes, vital signs, personal statistics, etc. The forms follow a strict format and are automatically arranged by the EHR software.
Better Patient Confidentiality
Paper charts and documents are more at risk of tampering or a privacy breach. EHR systems, however, have safeguards which flag any attempt to access the records made by an unauthorised party.
Error Reduction
Implementing EHR can reduce errors like misinterpreted handwriting, incorrectly entered ordered, transcription errors etc. The use of tools like barcodes and flagging code makes sure no patient details are missed or overlooked.
Efficiency
EHR benefits include quicker documentation, real-time data uploading and updates, remote access, reminders, trigger warning for flagged circumstances, reduced wait time and bill processing time, etc.
Overall, it leads to a better equipped, more efficient system.
Cons
Privacy Concerns
Recent cases of data breaches at supposedly secure data repositories in the financial and banking sector raise questions about the safety of patient information stored in a digital record. The concerns are related to information transfer over the internet and the effectiveness of the regulations which govern the assessing, authentication, auditing, transmittal, and storage of electronic health records.
Interoperability
It’s tough to reach an architecture that can ensure reduced ambiguity and better workflow between the EHR system providers in the Health IT industry. In cross-border cases, interoperability issues also arise because of fundamental legal incompatibilities.
Over Standardisation
We haven’t yet attained an EHR model that takes all the medications and treatments into account. In cases where a lesser used entity which isn’t a part of the EHR system is to be included, the workaround needed to fix it may waste time.
Setup and Maintenance Cost
It’s often difficult to justify the expenses of an EHR, especially for practices with thin margins.
Every medical assistance office must conduct a cost-benefit analysis, take out an ROI forecast, and determine how long they intend to use the service before purchasing.
B) Electronic Medical Records or EMR
An EMR is not to be used interchangeably with an EHR.
- An EMR is a narrow view of any patient’s health history while an EHR is comprehensive.
- Individual medical service providers own an EMR while an EHR is owned by hospitals and shared among practices.
- An EMR is like a digital clinical chart while an EHR is a patient’s well-detailed medical history.
Pros
Financial Benefits
According to a report published in the American Journal of Medicine, providers who used EMR applications saved money on drugs and radiologic diagnostics. They also reported decreased billing errors and upgraded bill recording and reporting services.
Improved Patient Care
The EMR systems send clinical summaries to the patients within a few days of their visit. It includes details regarding their visit, prescriptions, medical advice, and dates for follow-up appointments.
EMR software systems also provide links to texts and videos related to patients’ health conditions.
It tracks data and results over time. It automatically identifies patients who are due for screening and sends reminders.
Better Quality of Care
An EMR is designed to increase the engagement of patients with the clinic. It is primarily used for diagnosis and treatment purposes. It also helps focus on preventative care and encourages healthier lifestyles for the patients.
Going paperless can help by removing the errors caused by illegible scripts and misinterpreted prescriptions. It streamlines the office workflow, eliminating several redundant tasks.
Cost-Effective
The gross transcription costs and supply expenses go down. Automated scheduling and billing tasks save time.
Cons
Technical Difficulties
The EMR software could be vulnerable to hackers because of inefficient bug fixes and lack of constant upgrades. In the absence of system-wide software and hardware updates, the EMR system could crash. Several users complain of the problematic user experience, frequently lost access to the system and technical failures.
Every practise using EMR must regularly back up the data and have a restoration policy ready for an emergency.
Security
The degree of safety of an EMR system greatly depends on the provider. Medical offices must use a secure server, password-protected transactions, and strong passwords which are changed at regular intervals.
Steep Learning Curve
It can take time to teach the users to operate an EMR system. The training process will also require changes in work practices. The cost of EMR training may put a dent in a medical office’s finances.
Transfer of Information and Medical Reports
One of the major concerns with EMR is its inability to share information between two different practises. The client reports to be shared between two medical offices must be printed out under the current policies, considering that different healthcare centres use different EMR providers who may be unable to communicate with each other effectively.
However, the federal government has mandated the introduction of cross-EMR communication feature in the future and companies are working to follow up.
C) PHR or Personal Health Records
Ideally, it’s supposed to be an accurate and complete summary of a person’s medical history. It’s recorded online and may include lab results, patient-reported data, allergies, medications, surgeries, vaccinations, the result of smartphones based health devices and electronic weight or blood pressure calculators, etc.
The low-cost, reliable, and traditional method of storing personal health information by individuals initially involved printed reports and receipts. PHR improved on this system by introducing personal web-based solutions with the ability to record, encrypt, take the backup, print, and import health-related data.
Pros
Single Data Store for Personal Health Information
It’s a neat compilation of every health-related detail of an individual. It’s accessible at all times. And, it gives people control over the accuracy and reliability related to their medical history.
Better Patient Care
A Tethered PHR is connected with EHRs. Providers are allowed to place patient-related data in the specific PHR. It’s beneficial as it enables streamlined communication between hospitals and patients with least obstruction.
Even if people use an Untethered PHR, which isn’t connected with EHRs, they can choose to offer their records to a hospital in case of an emergency or regular visit for better care.
Cons
Digital Divide
The world still deals with issues like low computer literacy levels and limited access to computers and internet, especially in cases of low-income families and the elderly. Owing to similar reasons, Google discontinued Google Health, its PHR service in 2012.
Adoption Barriers
Most people do not record every healthcare experience detail, hence leading to the misutilisation of web-based PHRs.
Functional Restriction
Many PHR providers offer a few functionalities to the users, including the data entry fields, validation forms, etc. Studies by groups like Cleveland Clinic and Kaiser Permanente revealed that an increase in PHR usage is directly affected by the addition of features that users require.
Security
Patients are worried about the protection of their health information. Reasonably so, considering the heightened cases of network computer break-ins, unauthorised access, accidental disclosure, misuse of information by the medical personnel, hardware theft, etc.
4) Scheduling Software

Improving communication between health care providers and health information technologies is essential to define a perfect model of medical care. Scheduling software can help by offering easy access to the schedules of physicians. The service is also conveniently available over mobile devices.
Pros
- Less juggling required for the on-call doctor’s schedule
- On-call scheduling software can help the ER personnel manage more effectively
- Real-time updates available on a web portal reduce the stress of constantly checking the email or worrying about the accuracy of a schedule
- Scheduling software better arrange the time of medical professionals, reducing their stress and giving them enough breaks to manage a functional work-life balance
- The saved time and more efficient management ultimately lead to monetary benefits
Although, before implementing a medical scheduling software, it is critical for administrators to determine the need.
An online appointment app, for instance, will be beneficial in urban areas but not so much for the rurals with little to no internet access or computer literacy. Patient demographics, facility location, server security, nightly backups, etc. are significant factors to be considered before buying the services of any medical scheduling software.
Healthcare Information Technology System- Is It the Best of Both Worlds as Advertised?
IT healthcare is about incorporating hardware, network and software solutions to improve medical ecosystems.
In a shell, it’s meant to-
- Empower the patients
- Assist the service providers in managing patient care
- Improve the accuracy of treatments
- Enhance the efficiency of proceedings
- Encourage more cost-effective healthcare systems
We are deep into the phase where Health IT is being implemented increasingly. In fact, according to the ‘2017: The Year Ahead in Health IT’ survey held by Healthcare IT News, healthcare executives are constantly hunting for upgrades to improve their IT programmes.
The future of healthcare isn’t about eliminating medical practitioners; it’s about leveraging them by providing smarter digital tools, uber-supportive environments, organised data, and efficient services.
— James Madara, Executive VC MD, & CEO, AMA,
That does mirror the ‘best of both worlds’ sentiment.
Similar Posts

How Can Small Business Cope With The Long-Term Effects Of Covid-19?
The Covid-19 crisis has been disruptive for many businesses, but the SMBs have had the major burn of all. There has been some relief in 2021 as the vaccines are here, and the lockdown has been removed. But things are still far from ordinary. And according to experts, it can be until august 2021 to […]...

Telehealth Development- Transforming the future of healthcare
Telehealth is transforming how we get healthcare, and it is at the forefront of that shift. Telehealth, also known as telemedicine or e-health, is revolutionizing the healthcare industry by using technology to connect patients with medical professionals virtually. With the increasing demand for healthcare services and the limited resources available, telehealth has become an important […]...

Telehealth Software: A Revolutionizing Technology For Healthcare Industry
The relationship between healthcare and technology always has an active status. But the immediate demands and uncontrollable situations of coronavirus pandemic deepen the bond towards a more permanent status. ...








